This page shows results related to Betapace and Cardiac Failure Congestive from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (AERS).
Click here to learn about all Betapace adverse events.Age
| GenderMale: 48% 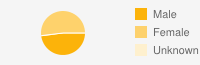 | ||||||||||||||||
OutcomeWhat were the most common outcomes of those reporting Cardiac Failure Congestive?
| ReporterWho most commonly reported Cardiac Failure Congestive?
| ||||||||||||||||
TherapyOf those reporting Cardiac Failure Congestive, why were they taking Betapace?
|
The Naranjo Scale is a questionnaire for determining the likelihood of whether an adverse drug reaction is actually due to the drug or caused by other factors. Probability is assigned via a score termed definite, probable, possible or doubtful.*
| YES | NO | UNKOWN | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Are there previous conclusive reports on this reaction? | |||
| Did the adverse event appear after the suspected drug was administered? | |||
| Did the adverse reaction improve when the drug was discontinued or a specific antagonist was administered? | |||
| Did the adverse reaction reappear when the drug was readministered? | |||
| Are there alternative causes (other than the drug) that could on their own have caused the reaction? | |||
| Did the reaction reappear when a placebo was given? | |||
| Was the drug detected in the blood (or other fluids) in concentrations known to be toxic? | |||
| Was the reaction more severe when the dose was increased, or less severe when the dose was decreased? | |||
| Did the patient have a similar reaction to the same or similar drugs in any previous exposure? | |||
| Was the adverse event confirmed by any objective evidence? |
*Naranjo, et al. "A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions." Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Aug;30(2):239-45.
To learn more about all adverse events for Betapace, view the complete Betapace adverse event report.
Share your experience with Betapace and Cardiac Failure Congestive.